SGA-Clock
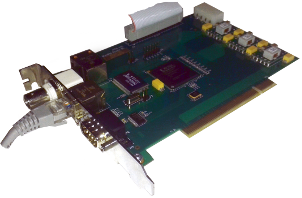
One of the most important factors of network traffic monitoring is accurate timestamping. SGA monitoring devices support multiple methods from plain software solutions to high precision hardware based time synchronizations. Our answer to these questions is an FPGA-based centralized timing server card. All SGA devices connect to one master Clock-card. Extension boards can be inserted for further clock distribution if needed. The heart of the SGA-Clock card is a cost effective, but powerful Spartan 6 FPGA processor. Supported time synchronization protocols span from plain NTP over PTP to GPS.
Main functions:
The two main functions of the SGA-Clock card are:
- the card's main clock is synchronized to a reference clock over a dedicated network connection (fe. by using NTP protocol). This function is implemented in FPGA.
- precise time source for all SGA cards and devices (SGA-10GED, GPLANAR, C-GEP, ...)that are connected to the SGA-Clock. A distributed master-slave interface structure ensures stable and reliable synchronization.
Card Components
- Dual 10/100/1000 Mb/s RJ45 receptacle
- GPS PPS or G703 signal input
- PCI Connector feeding 12V power rail only
- 40 pin BERG type Feature Connector (for master/slave communication)
- RTL8212 Dual 10/100/1000 Mb/s Ethernet transceiver
- Xilinx Spartan 3AN family FPGA device
- JTAG connector for programming the FPGA or Flash
- RS232 interface (NMEA/console)
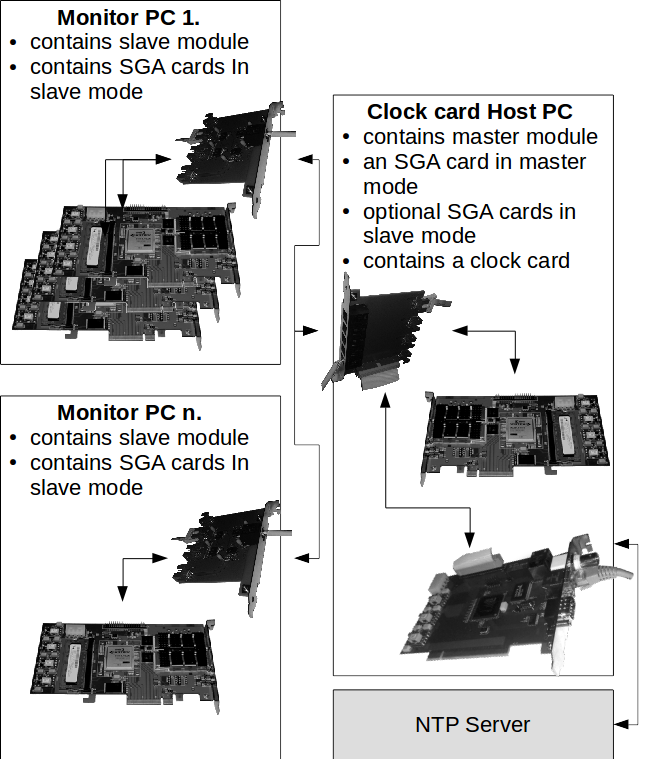
Clock card application example:
The SGA Clock-card provides reliable and coherent timestamp synchronization for a monitoring system consisting of many SGA monitoring-cards. In this case the Clock card is connected to a master panel which is responsible for distribing time synchronization across multiple monitoring probes. The monitoring PC-s have a slave panel for further internal timing distribution.
Block diagram of the Clock cards firmware functions:
The following picture shows the NTP synchronization realized in the FPGA firmware:
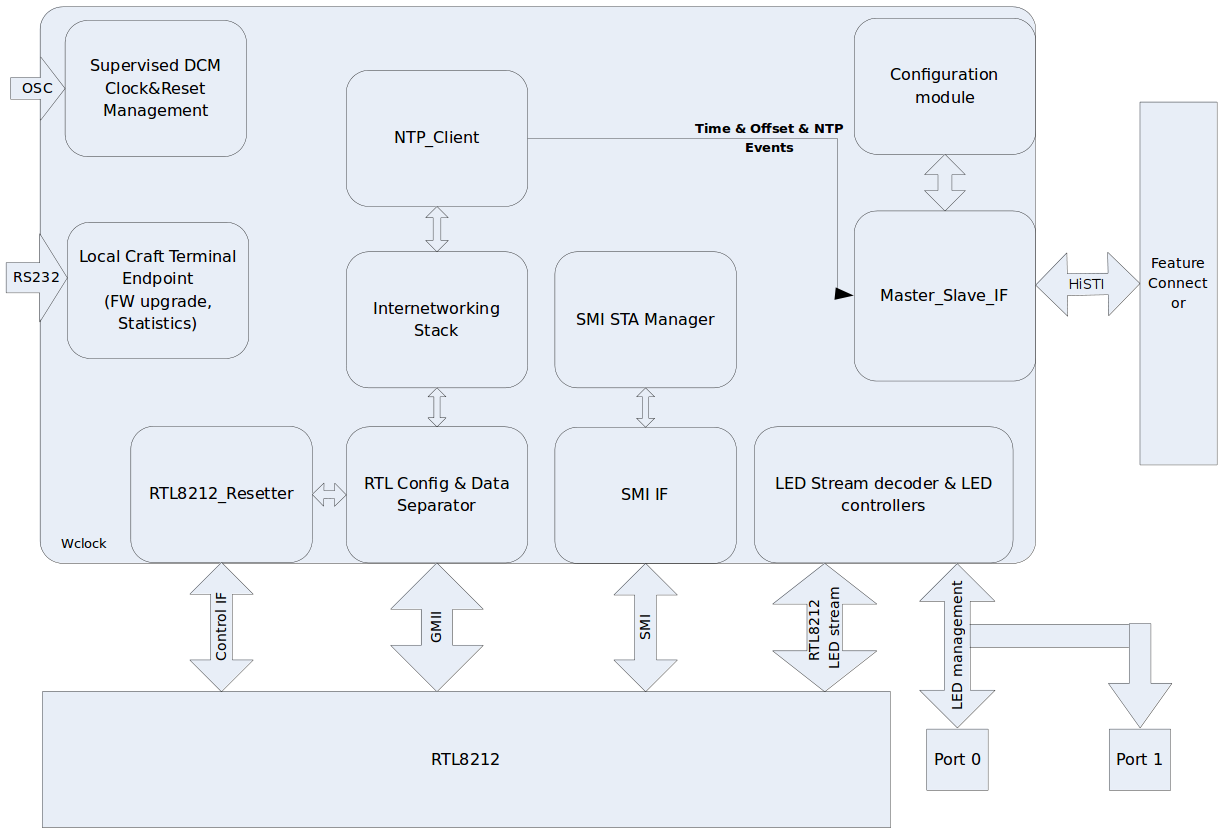
- Supervised DCM: clock management, and global reset
- Local craft terminal: RS232 software management, firmware upload
- RTL Config and Data separator: interface to the RTL8212 1G Ethernet chip
- RTL8212_Reset: Resets the RTL8212 interface chip
- SMI IF: Serial management implementation according to IEEE 802.3
- SMI STA Manager: Station manager as defined by IEEE 802.3
- LED controller: Controls the link and status LEDs
- Internetworking stack: generic 802.3 compatible modular Ethernet/ARP/IP/UDP protocol stack and MAC module
- NTP_client: NTP client implementation, NTP peer module, NTP clock filter and clock discipline (control loop) functions
- Configuration module: manages connection settings, IP addresses, etc.
- Master-slace IF: Implements communication interface (HisTi) between the Clock card (master) and the monitor cards (slaves)
AITIA offers customers the freedom to customize the firmware for their requirements as needed.